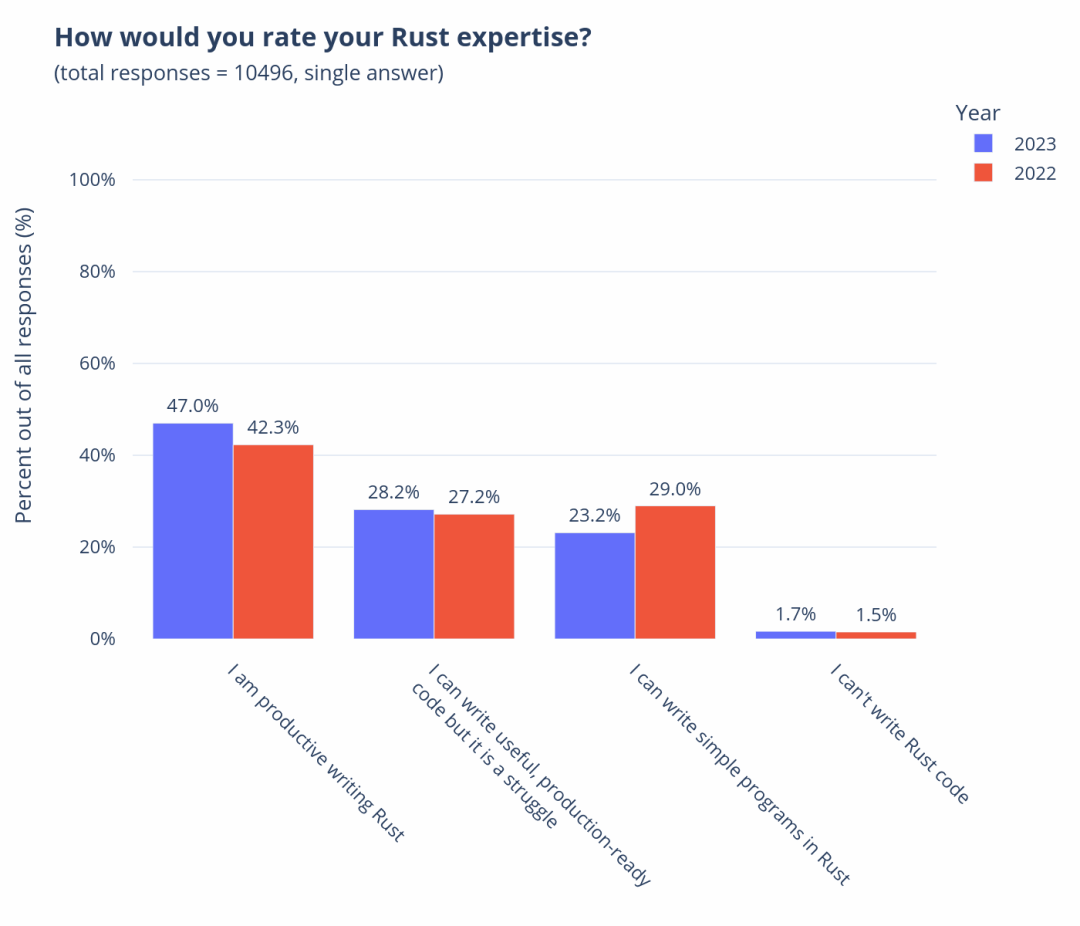
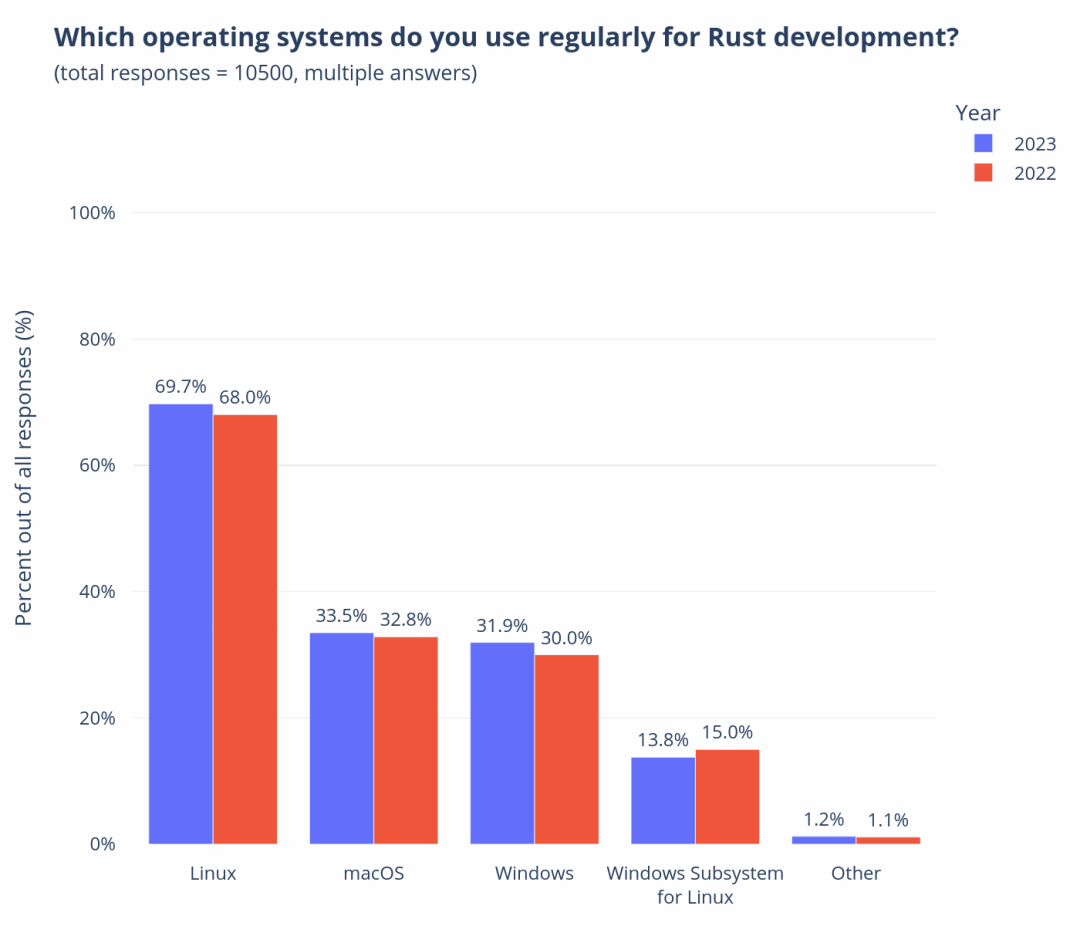
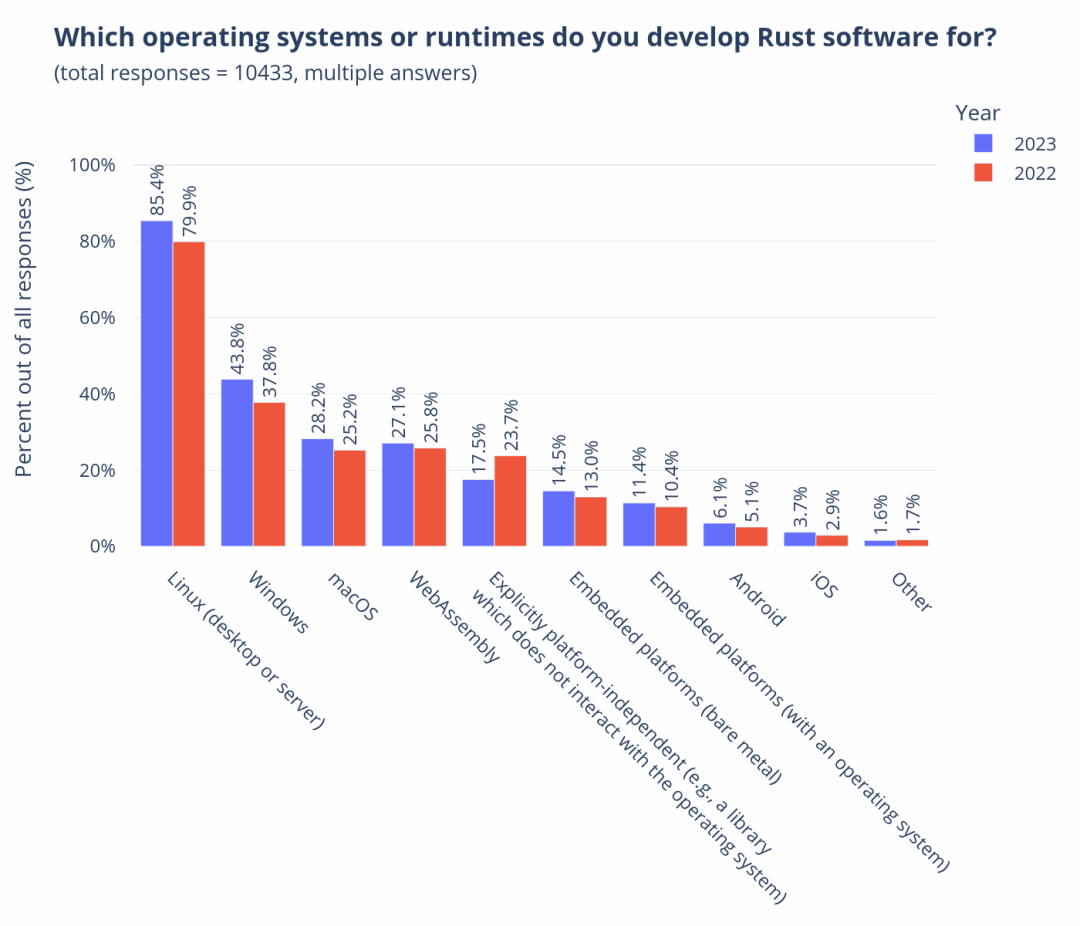
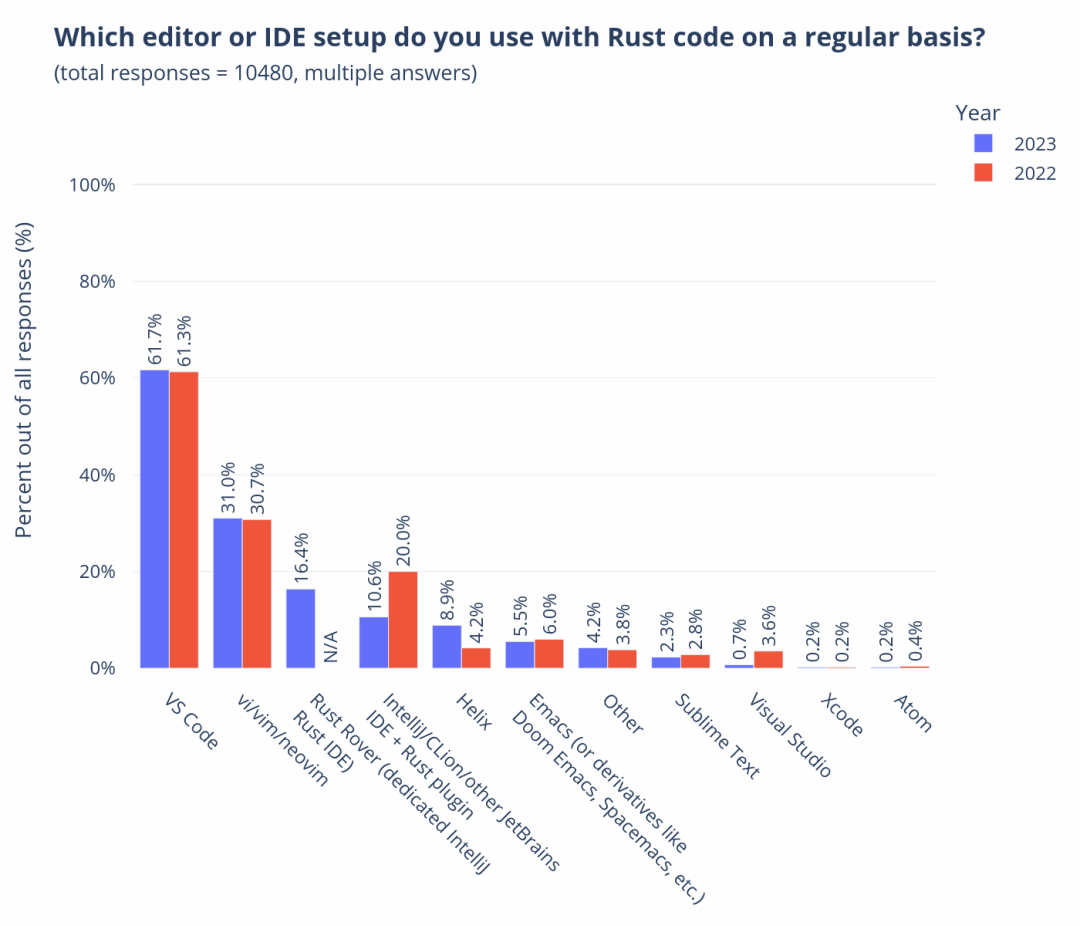
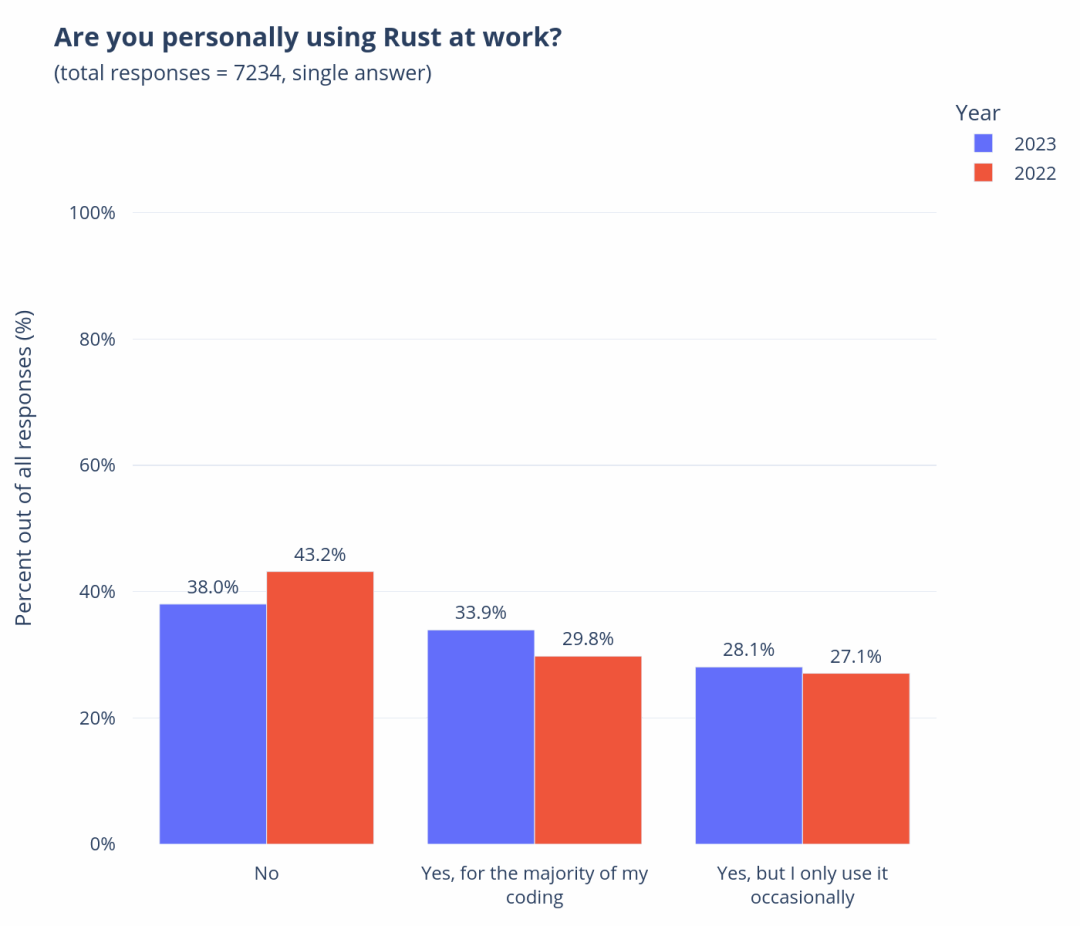
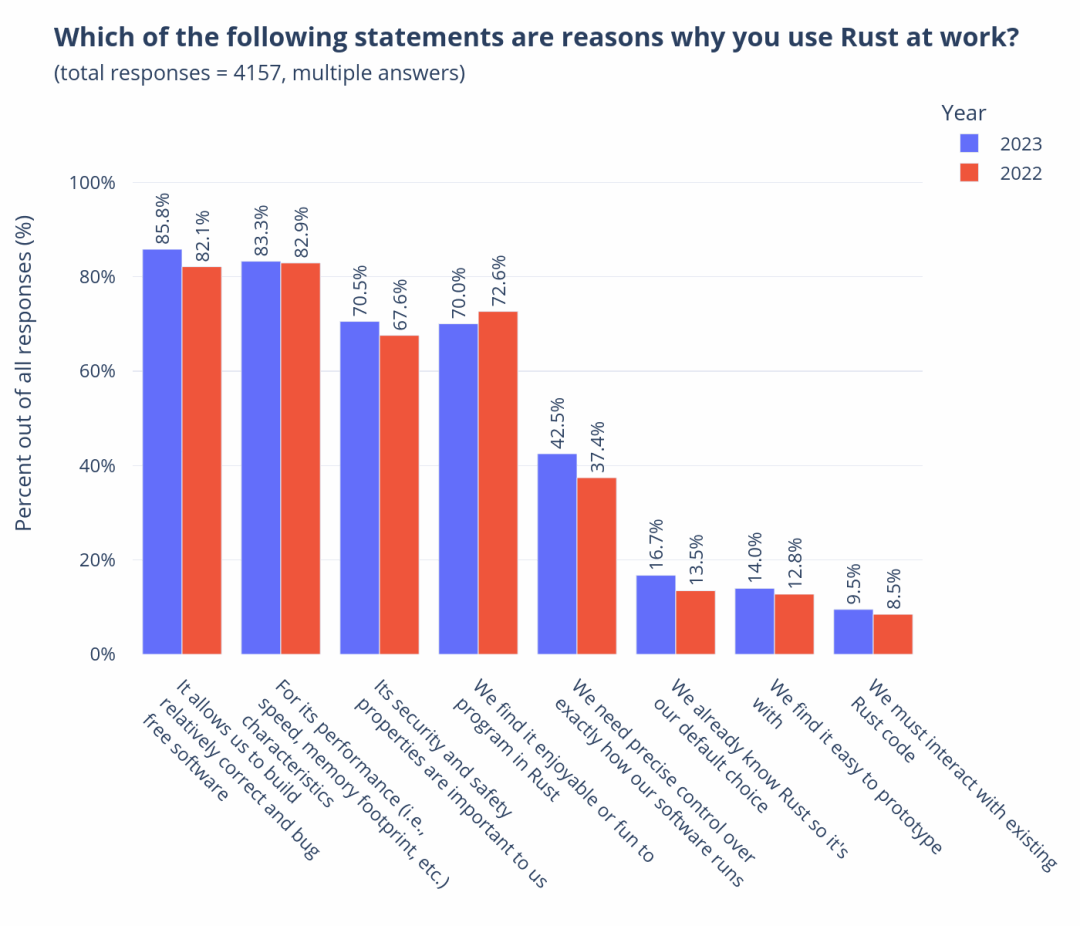
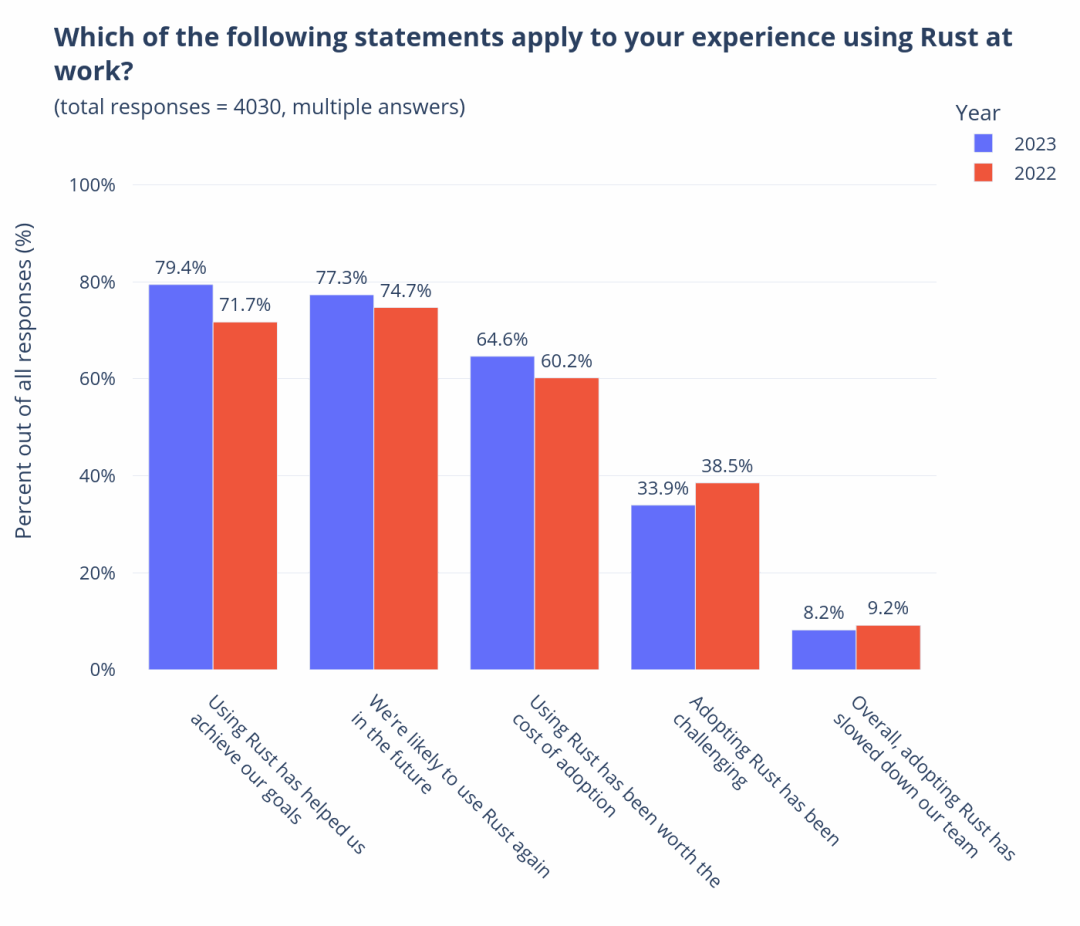
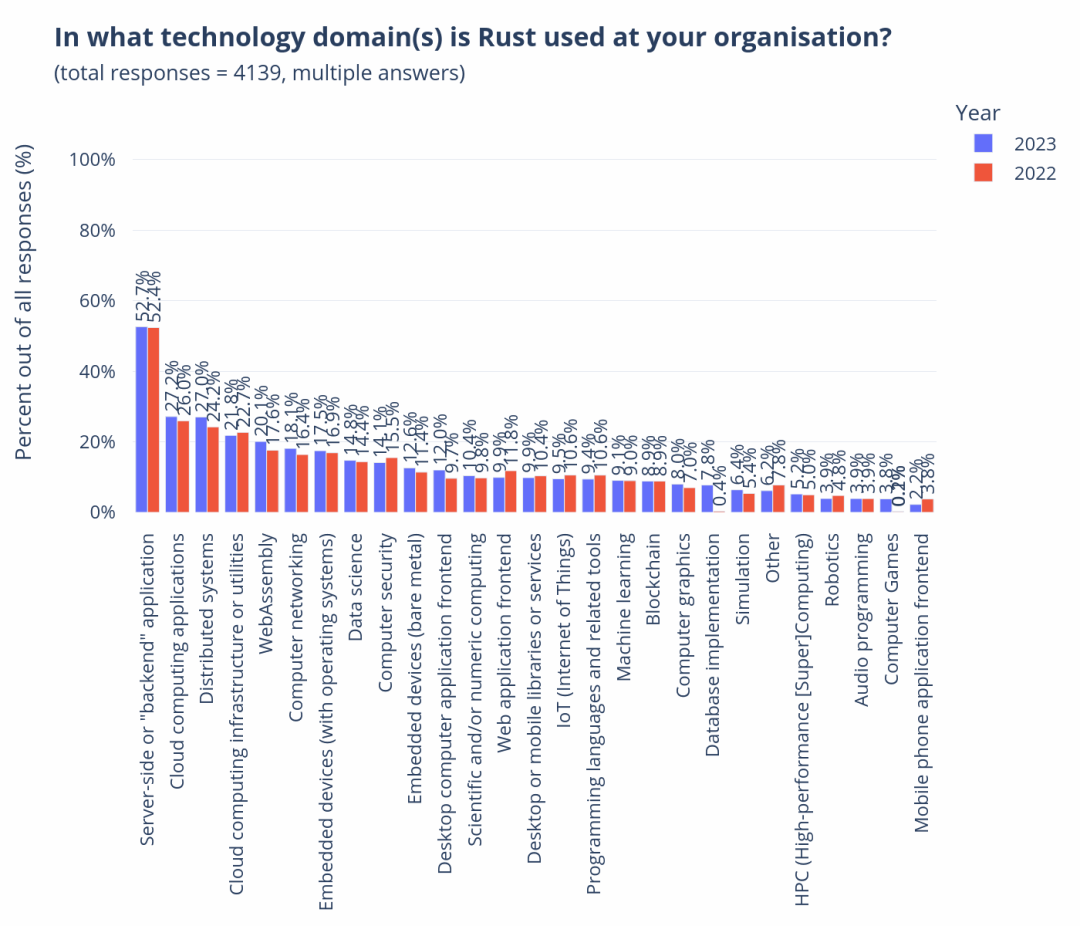
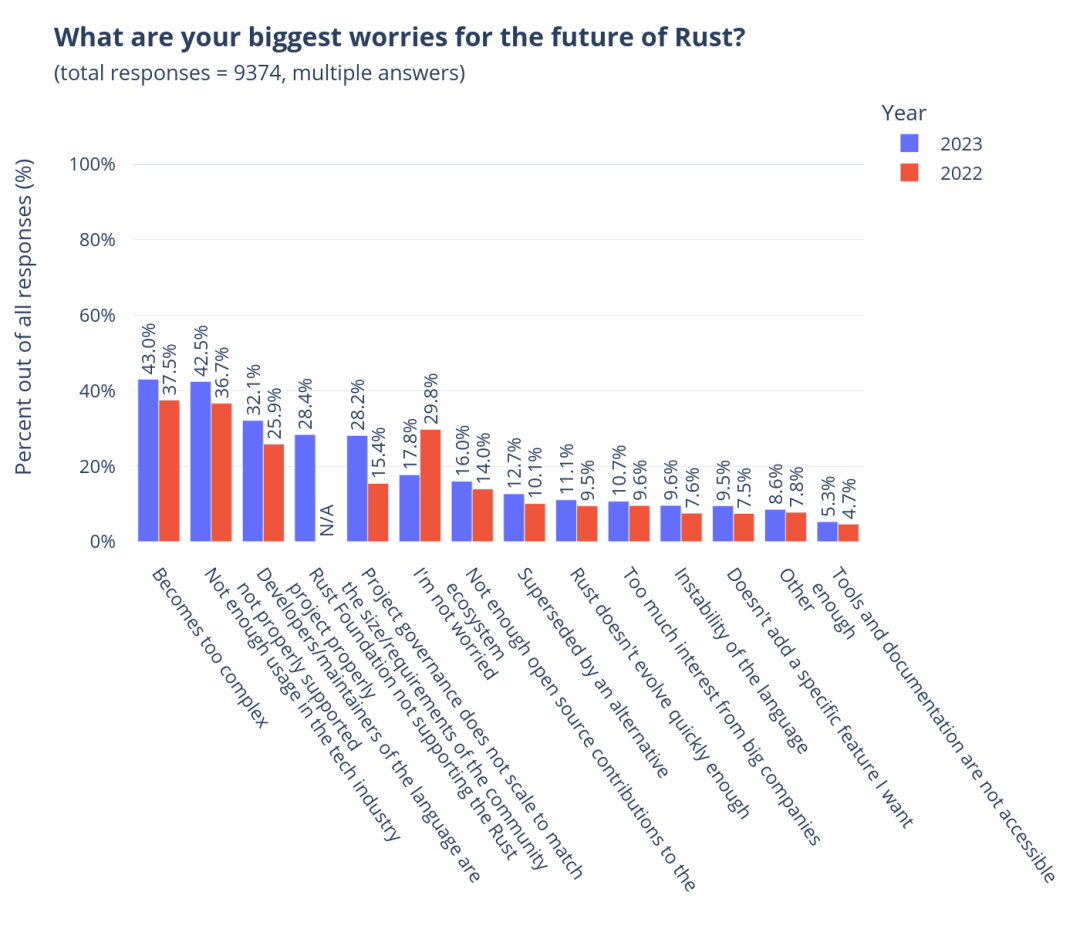
In the previous lecture, I introduced you to the overview and sources of our mid-platform building methodology. Starting from this lecture, I will take you through the four stages of our mid-platform planning and construction, introducing the goals of each stage and some commonly used tools and practices.
Okay, let’s start with the first stage of Discovery, which means we need to establish a “comprehensive perspective” on the enterprise and industry.
So why do we need to do this first? Let me add one more thing. In fact, the first two parts of D4, Discovery and Define, are a process of divergence and convergence at the enterprise level. Our company has a name for this process internally, called Portfolio Discovery, abbreviated as PD. In actual implementation, PD is a 4-8 week brainstorming workshop. The following figure shows a complete PD workshop roadmap to help you understand.
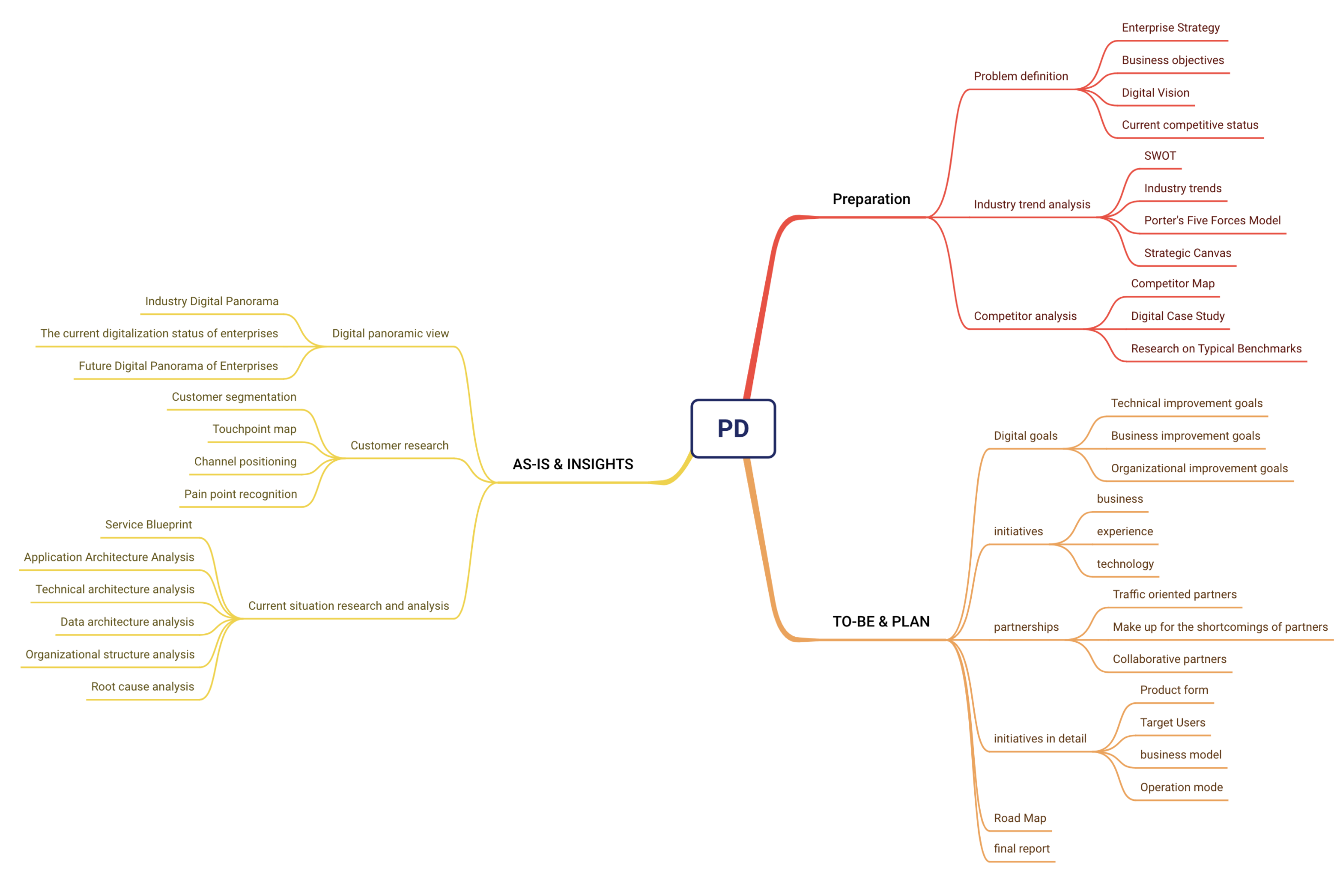
Regarding the overall planning of the middle platform, that is, answering questions such as whether to build a middle platform, which middle platforms to build, and who should build first and who should build later, we now evaluate and judge through the process of PD. You may have doubts about why PD, as a method, can help us make planning judgments for the middle platform. Here, we will briefly explain.
# Why use PD to plan the middle platform?
Portfolio Discovery is translated into Chinese as investment portfolio planning, which is equivalent to product line planning when applied in enterprises. To put it bluntly, if I am the CIO of a company and have a disposable IT budget of 100 million yuan this year, what I am most concerned about is in the next period of time (which may be 1 year or 3-5 years), in order to achieve the goal of enterprise development.
- How much money do I need to spend on digital construction?
- How should this money be spent? How should it be allocated? Which systems should be added, purchased or self-developed? Which systems should be eliminated? Which systems should be optimized? Which systems should be maintained? Which systems should be kept unchanged?
- Do you want to build a middle platform?
- ……
You see, to put it simply, it’s still a matter of how to spend money wisely. Essentially, it’s also a matter of quotas. How to find the best investment portfolio with limited resources, or how to spend money where it should be spent.
And building a middle platform is just one of the potential options. One of the potential solutions is to add a middle platform layer to the application architecture based on the enterprise’s strategy and current situation to solve the problems currently encountered by the enterprise.
Whether the mid-platform solution is suitable for enterprises or not still needs to be researched and judged. Therefore, if we take the mid-platform as a definite direction from the beginning, it will inevitably limit our vision, and we may miss better, simpler, and more effective solutions than the mid-platform, or over-design too early, and carry out mid-platform building in a scene where the mid-platform is not needed, which is a waste of time and money.
Should the company allocate a portion of the money and resources for mid-platform building? What is the value of adding a new architecture layer like a middle platform for the company? When is the best time to do it? What is the priority? These are also the questions that PD mainly focuses on and needs to answer.
In order to avoid impulsive situations, the main purpose of Discovery as a PD in the first half is to conduct sufficient divergence and research, that is, to use various tools and means to help us fully understand industry trends, competitor situations, company strategic decomposition, and bottom-up current situation research and other information and environment, in order to provide sufficient information support and basis for the convergence of the next stage of Define, that is, for the design of new business architecture, application architecture, technical architecture, and even organizational structure of the enterprise.
Overall, Discovery can be simply divided into three different directions: from outside to inside, from top to bottom, and from bottom to top.
# From the outside to the inside: industry and competitor analysis
Knowing oneself and the enemy leads to victory in a hundred battles. Before understanding ourselves in detail, it is necessary to broaden our horizons and see what the industry’s major trends and competitors are doing.
I remember that Teacher Liang Ning once mentioned the theory of “point-line-surface-body” in his column “30 Lectures on Product Thinking”. If the middle platform itself is just a point, then it may only be a product of a company’s development to a certain stage, not the beginning or the end. Therefore, we should look at the middle platform from the main line of a company’s development process and see where it comes from, why it appears, and where it will go. Even consider what the next stage of the middle platform will be and what it will be replaced by. I also look at it this way when observing the middle-platform building process of a company, including the formation and development of the entire middle platform trend.
Is having a line enough? Not enough. We need to take another dimension to see what other lines in the same industry, that is, what other companies in the same industry are doing? What are their strategies? What is the focus of digital construction? Are they also doing mid-platform building? What are the goals of the construction? What is the effect?
However, it should be noted that analysis does not necessarily mean direct reference. If others are building a middle platform, we should build one. This idea is not advisable because even in the same industry, due to differences in corporate vision, strategy, business model, customer base, etc., each company is different.
Finally, we need to step out and examine the industry itself from a higher dimension, or learn from other industries and aspects. There are generally two benefits to doing so.
- First, if there are good concepts or methods in other aspects, we can learn from them to help our own enterprises gain an advantage in their own industries. The concept of middle platform originated in the Internet industry and is currently being referenced and borrowed by various industries.
- Another benefit is that if you find a better surface and a better industry, you can realize the leap of the enterprise across industries, and you may seize the opportunity to enter another fast lane. That being said, at present, the purpose of many enterprises’ mid-platform building is to identify the core capabilities of the enterprise, sediment them into the middle platform, and use it as a springboard and support to carry out business innovation and exploration, so as to jump to another more promising new track.
After talking about the benefits of industry research and competitor analysis, how to do it specifically? In fact, the industry has many very mature methods that you can use directly, such as the common ones: Five Forces Model, SWOT, Business Model Canvas, Competitor Product Line Analysis, Competitive Situation Analysis Matrix, etc .
# Top-down: Corporate Strategy Decomposition
If the main output of PD is the blueprint and roadmap for digital construction, then the input of PD is the vision and strategy at the enterprise level.
We have talked a lot about vision before, which should be relatively easy to understand. It refers to the image or goal that we hope the company can become after a certain period of time. For example, in the case of Geek Real Estate, the vision may be to achieve the transformation of business from heavy assets to light assets by 2022. More specifically, the proportion of service business in total revenue should reach more than 70%.
Let me add one more thing here. We have indeed seen many companies start large-scale mid-platform building without a clear corporate vision. It’s like a fleet going out to sea without a clear destination, which may lead to being lost in the ocean and running out of ammunition. Therefore, if a company is in this situation, it must first supplement this part of the content.
Here, let’s assume that the company already has a clear vision and strategy as input for PD before starting the planning process.
Looking at the word “strategy” again, our understanding may seem vague and abstract. In the book “On Grand Strategy”, it is mentioned that “strategy refers to how to achieve a balance between goals and capabilities, and make appropriate adjustments according to environmental changes.”
Here is the strategic balance triangle that we often use, which can help you understand the relatively abstract concept of strategy.
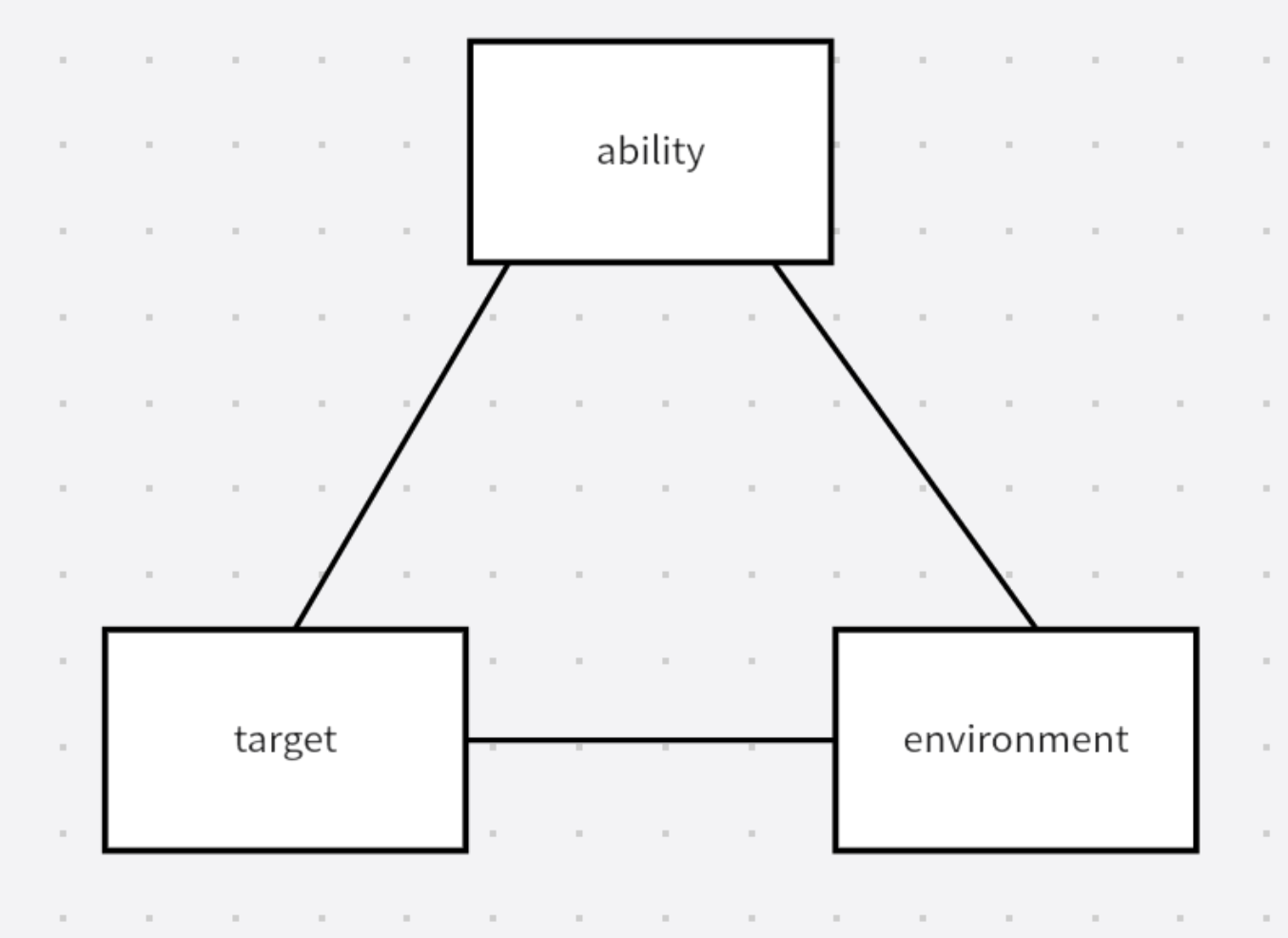
Through this strategic balance triangle, we can simply make some mathematical transformations to explain what “enterprise strategic decomposition” really is. The following derivation process may be a bit brain-burning. If you can’t understand it at the moment, you can read it several times. I believe it will be very helpful for you to understand the word “strategy”.
Okay, let’s get started. Based on the strategic balance triangle, with the company’s vision and goals already determined:
- Enterprise strategy can be simplified to understand: combined with the enterprise’s own capabilities and the environment in which it is located, what measures need to be taken to achieve the enterprise’s predetermined vision and goals?
- And the enterprise strategy decomposition can be simplified to understand: combined with the ability of the enterprise departments themselves and their environment, what kind of measures need to be taken to achieve the enterprise’s predetermined vision and goals?
Okay, the deduction is complete. There are many tools and practices in the industry for decomposing corporate strategy, such as the corporate strategy analysis model designed by BMGovernance. However, in order to cope with the rapidly changing market environment, we use the Lean Value Tree tool in PD to help decompose the strategic vision.
Lean Value Tree is a value-based tool used to analyze and communicate business vision, strategy, and investment. Its core is to establish a top-down alignment from vision, goals to investment initiatives, so it adopts a hierarchical tree structure, as shown in the following diagram.
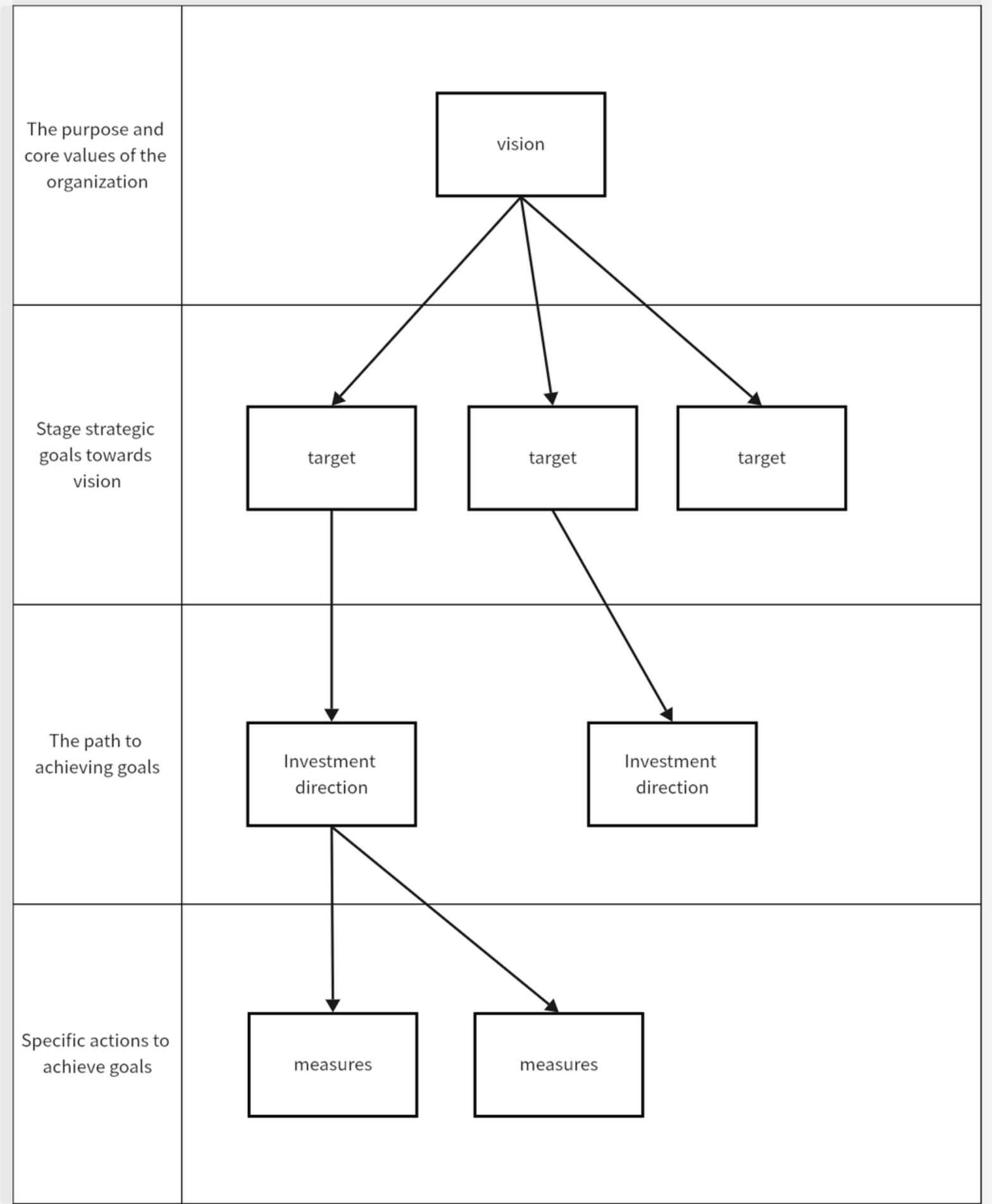
This process is what I call a top-down strategic decomposition process. For a certain middle platform, it may only be a specific measure that is ultimately derived. Upward, it still needs to be traced back to the relevance and value of the company’s vision and goals, and match and correspond to the company’s vision and goals.
# Bottom-up: Current Situation Research and Analysis
If we understand the decomposition of corporate strategy as a top-down analysis and deduction process from the corporate vision, can we simply implement the derived measures?
Often it is not enough, because every enterprise that has survived and developed in the market for a long time will encounter various problems and limitations. If they deviate from the status quo and ignore these problems and limitations, they will definitely face great resistance and risks.
Therefore, we not only need to decompose the enterprise strategy from top to bottom to help us think about whether it is necessary to take the middle platform or other measures, but also need to fully conduct bottom-up current situation research to help us understand the current situation and history. On the one hand, we fully respect all the problems encountered in the past, collect and summarize pain points; on the other hand, we are required to break free from past limitations, start from the business and users, and explore new possibilities based on new technologies and architectures.
Here we often use many tools and practices, such as high-level interviews, stakeholders maps, organizational structure analysis, strategic design thinking, business architecture status quo sorting, user journey, service blueprint, domain-driven design, application system status quo sorting, technical architecture status quo sorting, and so on.
Adequate and multi-dimensional current situation research and analysis not only allows us to have a comprehensive and clear understanding of the current situation of business, applications, technology, data, and organization, that is, the current situation of enterprise architecture, but also supplements the context of the timeline through interviews and research, including what happened in the past, why the current situation is like this, what kind of future everyone hopes for, and why.
However, there is one issue you may need to pay attention to here, which is the scope and depth of the sorting. Don’t forget that we are currently doing enterprise-level architecture sorting, and the width and scope may far exceed our imagination. If the depth is not well controlled, you will find that you are still spinning in a small field and Line of Business.
Therefore, in the face of such problems and risks, I suggest that you:
- First, complete the top-down decomposition of the enterprise strategy, and then conduct a bottom-up current situation investigation. After completing the strategic decomposition, we already have some understanding of the company’s industry, business, vision, and strategy. When conducting the investigation, we will have a global control, making it easier to grasp the granularity and depth.
- Make sufficient preparations and complete the content that can be completed in advance through reading materials and small-scale research.
- Make a detailed plan, and you can reverse engineer the scope and granularity of sorting according to the total time of the current investigation. If there is enough time, you can spend two days to sort out the business architecture of a Line of Business, so that the sorting can be deeper. But if there is only half a day, the granularity can be appropriately bolded to ensure that there is a global business view.
- It is suggested that at the beginning, the granularity can be coarser, and do not get too caught up in details too early. However, how to control the granularity does require a deep understanding of the company’s strategy and business, which is also the most effective part. When the judgment is not good, it can be coarser first. If there is still time in the end, another round of research can be conducted to expand further.
For a medium-sized enterprise with four or five different Lines of Business, it usually takes about 2-4 weeks to implement such a current situation survey, depending on the client. After completing the survey, we have a comprehensive understanding of the current situation of the enterprise in all aspects, and have also collected a large number of pain points and problems for each Line of Business, which provides a prospect for the future architecture.
When doing bottom-up research on various Lines of Business, the tools we use are not traditional business process diagrams, but are combined with the idea of design thinking, using the way of combining user journey with service blueprint . The specific content will be introduced to you when introducing the design process of a Central Product Platform in 08.
# Summarize thinking
So far, we have conducted industry analysis from the outside to the inside, competitor research, top-down enterprise strategy decomposition, and bottom-up investigation of various dimensions of the enterprise based on the current situation, and have made sufficient divergence to collect sufficient information.
We conducted the entire PD process (including the Define process to be discussed in the next lecture) in a workshop format, where relevant roles brainstormed and fully discussed together to produce the final result. The entire process was very lightweight and efficient.
After completing the first half of Discovery in PD, the next step is to analyze and integrate the collected raw material information to form a specific mid-platform building plan, which is the second half of PD, the process of Define. I will introduce it to you in the next lecture.
Finally, I’ll leave you with a few thinking questions:
- What is the vision of your company? What is the strategy? When it comes to your department, what are the measures?
- Does your company really need to build a middle platform? Can it match the company’s vision?